0 사전 작업
라즈베리파이에 Node-RED가 (도커 방식이 아닌) 일반 방식으로 설치되어 있어야 합니다.
1 사용자와 비밀번호 등록하기
Node_RED를 처음 설치하면 접속 제한이 되지 않으므로 누구든지 접속할 수 있습니다. 여기서는 Node-RED에 사용자 ID와 비밀번호를 등록하는 방법을 안내합니다.
만약 Node-RED가 외부 네트웍에 노출된다면 최소한 사용자 ID와 비밀번호를 사용해서 접속을 통제해야 합니다.
Node-RED 명령어 설치하기
비밀번호 해시 명령어를 사용하기 위해서는 Node-RED 명령어를 한 번 설치해야 합니다. 아래의 명령어를 입력합니다.
npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-red-admin
Node-RED 비밀 번호 해시 만들기
만약 비밀 번호 gildongcoolguy의 비밀 번호 해시를 만들고 싶으면 다음과 같은 명령어를 입력합니다.
node-red-admin hash-pw
이 명령어를 실행하면 비밀번호를 요구합니다. 이 때 gildongcoolguy을 입력하면 암호화된 비밀번호가 다음과 같이 출력됩니다.

출력된 해시 비밀번호는 다음 단계에서 사용해야 하므로 보관해 두어야 합니다.
$2b$08$q9jgUlHa4acWMtPPBYQI0.DxrfKQuthuUuwecy2xhSZLlvAXmmSKm
이 처럼 해시 비밀 번호는 몇 개든지 만들 수 있습니다.
settings.js 파일 수정하기
sudo nano .node-red/settings.js
다음과 같은 편집 화면이 나타납니다.
다음은 .node-red/settings.js의 소스 파일입니다. 만약 파일이 없으면 디렉토리를 만들고 파일을 복사하여 만들어야 합니다.
/**
* This is the default settings file provided by Node-RED.
*
* It can contain any valid JavaScript code that will get run when Node-RED
* is started.
*
* Lines that start with // are commented out.
* Each entry should be separated from the entries above and below by a comma ','
*
* For more information about individual settings, refer to the documentation:
* https://nodered.org/docs/user-guide/runtime/configuration
**/
module.exports = {
// the tcp port that the Node-RED web server is listening on
uiPort: process.env.PORT || 1880,
// By default, the Node-RED UI accepts connections on all IPv4 interfaces.
// To listen on all IPv6 addresses, set uiHost to "::",
// The following property can be used to listen on a specific interface. For
// example, the following would only allow connections from the local machine.
//uiHost: "127.0.0.1",
// Retry time in milliseconds for MQTT connections
mqttReconnectTime: 15000,
// Retry time in milliseconds for Serial port connections
serialReconnectTime: 15000,
// Retry time in milliseconds for TCP socket connections
//socketReconnectTime: 10000,
// Timeout in milliseconds for TCP server socket connections
// defaults to no timeout
//socketTimeout: 120000,
// Maximum number of messages to wait in queue while attempting to connect to TCP socket
// defaults to 1000
//tcpMsgQueueSize: 2000,
// Timeout in milliseconds for HTTP request connections
// defaults to 120 seconds
//httpRequestTimeout: 120000,
// The maximum length, in characters, of any message sent to the debug sidebar tab
debugMaxLength: 1000,
// The maximum number of messages nodes will buffer internally as part of their
// operation. This applies across a range of nodes that operate on message sequences.
// defaults to no limit. A value of 0 also means no limit is applied.
//nodeMessageBufferMaxLength: 0,
// To disable the option for using local files for storing keys and certificates in the TLS configuration
// node, set this to true
//tlsConfigDisableLocalFiles: true,
// Colourise the console output of the debug node
//debugUseColors: true,
// The file containing the flows. If not set, it defaults to flows_<hostname>.json
//flowFile: 'flows.json',
// To enabled pretty-printing of the flow within the flow file, set the following
// property to true:
//flowFilePretty: true,
// By default, credentials are encrypted in storage using a generated key. To
// specify your own secret, set the following property.
// If you want to disable encryption of credentials, set this property to false.
// Note: once you set this property, do not change it - doing so will prevent
// node-red from being able to decrypt your existing credentials and they will be
// lost.
//credentialSecret: "a-secret-key",
// By default, all user data is stored in a directory called `.node-red` under
// the user's home directory. To use a different location, the following
// property can be used
//userDir: '/home/nol/.node-red/',
// Node-RED scans the `nodes` directory in the userDir to find local node files.
// The following property can be used to specify an additional directory to scan.
//nodesDir: '/home/nol/.node-red/nodes',
// By default, the Node-RED UI is available at http://localhost:1880/
// The following property can be used to specify a different root path.
// If set to false, this is disabled.
//httpAdminRoot: '/admin',
// Some nodes, such as HTTP In, can be used to listen for incoming http requests.
// By default, these are served relative to '/'. The following property
// can be used to specifiy a different root path. If set to false, this is
// disabled.
//httpNodeRoot: '/red-nodes',
// The following property can be used in place of 'httpAdminRoot' and 'httpNodeRoot',
// to apply the same root to both parts.
//httpRoot: '/red',
// When httpAdminRoot is used to move the UI to a different root path, the
// following property can be used to identify a directory of static content
// that should be served at http://localhost:1880/.
//httpStatic: '/home/nol/node-red-static/',
// The maximum size of HTTP request that will be accepted by the runtime api.
// Default: 5mb
//apiMaxLength: '5mb',
// If you installed the optional node-red-dashboard you can set it's path
// relative to httpRoot
//ui: { path: "ui" },
// Securing Node-RED
// -----------------
// To password protect the Node-RED editor and admin API, the following
// property can be used. See http://nodered.org/docs/security.html for details.
//adminAuth: {
// type: "credentials",
// users: [{
// username: "admin",
// password: "$2a$08$zZWtXTja0fB1pzD4sHCMyOCMYz2Z6dNbM6tl8sJogENOMcxWV9DN.",
// permissions: "*"
// }]
//},
// To password protect the node-defined HTTP endpoints (httpNodeRoot), or
// the static content (httpStatic), the following properties can be used.
// The pass field is a bcrypt hash of the password.
// See http://nodered.org/docs/security.html#generating-the-password-hash
//httpNodeAuth: {user:"user",pass:"$2a$08$zZWtXTja0fB1pzD4sHCMyOCMYz2Z6dNbM6tl8sJogENOMcxWV9DN."},
//httpStaticAuth: {user:"user",pass:"$2a$08$zZWtXTja0fB1pzD4sHCMyOCMYz2Z6dNbM6tl8sJogENOMcxWV9DN."},
// The following property can be used to enable HTTPS
// See http://nodejs.org/api/https.html#https_https_createserver_options_requestlistener
// for details on its contents.
// This property can be either an object, containing both a (private) key and a (public) certificate,
// or a function that returns such an object:
//// https object:
//https: {
// key: require("fs").readFileSync('privkey.pem'),
// cert: require("fs").readFileSync('cert.pem')
//},
////https function:
// https: function() {
// // This function should return the options object, or a Promise
// // that resolves to the options object
// return {
// key: require("fs").readFileSync('privkey.pem'),
// cert: require("fs").readFileSync('cert.pem')
// }
// },
// The following property can be used to refresh the https settings at a
// regular time interval in hours.
// This requires:
// - the `https` setting to be a function that can be called to get
// the refreshed settings.
// - Node.js 11 or later.
//httpsRefreshInterval : 12,
// The following property can be used to cause insecure HTTP connections to
// be redirected to HTTPS.
//requireHttps: true,
// The following property can be used to disable the editor. The admin API
// is not affected by this option. To disable both the editor and the admin
// API, use either the httpRoot or httpAdminRoot properties
//disableEditor: false,
// The following property can be used to configure cross-origin resource sharing
// in the HTTP nodes.
// See https://github.com/troygoode/node-cors#configuration-options for
// details on its contents. The following is a basic permissive set of options:
//httpNodeCors: {
// origin: "*",
// methods: "GET,PUT,POST,DELETE"
//},
// If you need to set an http proxy please set an environment variable
// called http_proxy (or HTTP_PROXY) outside of Node-RED in the operating system.
// For example - http_proxy=http://myproxy.com:8080
// (Setting it here will have no effect)
// You may also specify no_proxy (or NO_PROXY) to supply a comma separated
// list of domains to not proxy, eg - no_proxy=.acme.co,.acme.co.uk
// The following property can be used to add a custom middleware function
// in front of all http in nodes. This allows custom authentication to be
// applied to all http in nodes, or any other sort of common request processing.
//httpNodeMiddleware: function(req,res,next) {
// // Handle/reject the request, or pass it on to the http in node by calling next();
// // Optionally skip our rawBodyParser by setting this to true;
// //req.skipRawBodyParser = true;
// next();
//},
// The following property can be used to add a custom middleware function
// in front of all admin http routes. For example, to set custom http
// headers
// httpAdminMiddleware: function(req,res,next) {
// // Set the X-Frame-Options header to limit where the editor
// // can be embedded
// //res.set('X-Frame-Options', 'sameorigin');
// next();
// },
// The following property can be used to pass custom options to the Express.js
// server used by Node-RED. For a full list of available options, refer
// to http://expressjs.com/en/api.html#app.settings.table
//httpServerOptions: { },
// The following property can be used to verify websocket connection attempts.
// This allows, for example, the HTTP request headers to be checked to ensure
// they include valid authentication information.
//webSocketNodeVerifyClient: function(info) {
// // 'info' has three properties:
// // - origin : the value in the Origin header
// // - req : the HTTP request
// // - secure : true if req.connection.authorized or req.connection.encrypted is set
// //
// // The function should return true if the connection should be accepted, false otherwise.
// //
// // Alternatively, if this function is defined to accept a second argument, callback,
// // it can be used to verify the client asynchronously.
// // The callback takes three arguments:
// // - result : boolean, whether to accept the connection or not
// // - code : if result is false, the HTTP error status to return
// // - reason: if result is false, the HTTP reason string to return
//},
// The following property can be used to seed Global Context with predefined
// values. This allows extra node modules to be made available with the
// Function node.
// For example,
// functionGlobalContext: { os:require('os') }
// can be accessed in a function block as:
// global.get("os")
functionGlobalContext: {
// os:require('os'),
// jfive:require("johnny-five"),
// j5board:require("johnny-five").Board({repl:false})
},
// `global.keys()` returns a list of all properties set in global context.
// This allows them to be displayed in the Context Sidebar within the editor.
// In some circumstances it is not desirable to expose them to the editor. The
// following property can be used to hide any property set in `functionGlobalContext`
// from being list by `global.keys()`.
// By default, the property is set to false to avoid accidental exposure of
// their values. Setting this to true will cause the keys to be listed.
exportGlobalContextKeys: false,
// Context Storage
// The following property can be used to enable context storage. The configuration
// provided here will enable file-based context that flushes to disk every 30 seconds.
// Refer to the documentation for further options: https://nodered.org/docs/api/context/
//
//contextStorage: {
// default: {
// module:"localfilesystem"
// },
//},
// The following property can be used to order the categories in the editor
// palette. If a node's category is not in the list, the category will get
// added to the end of the palette.
// If not set, the following default order is used:
//paletteCategories: ['subflows', 'common', 'function', 'network', 'sequence', 'parser', 'storage'],
// Configure the logging output
logging: {
// Only console logging is currently supported
console: {
// Level of logging to be recorded. Options are:
// fatal - only those errors which make the application unusable should be recorded
// error - record errors which are deemed fatal for a particular request + fatal errors
// warn - record problems which are non fatal + errors + fatal errors
// info - record information about the general running of the application + warn + error + fatal errors
// debug - record information which is more verbose than info + info + warn + error + fatal errors
// trace - record very detailed logging + debug + info + warn + error + fatal errors
// off - turn off all logging (doesn't affect metrics or audit)
level: "info",
// Whether or not to include metric events in the log output
metrics: false,
// Whether or not to include audit events in the log output
audit: false
}
},
// Customising the editor
editorTheme: {
projects: {
// To enable the Projects feature, set this value to true
enabled: false
}
}
}
편집기에서 ▼, ▲ 키를 이용하여 다음 부분을 찾습니다. 이 때 편집기의 윈도우 화면은 최대한 크게 하는 것이 편합니다.
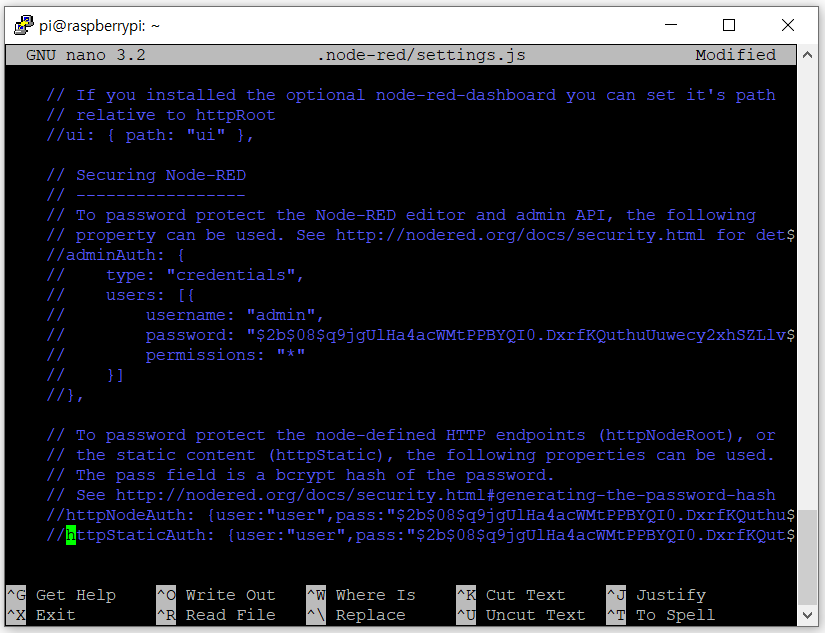
편집기에서 앞의 내용을 다음과 같이 수정합니다. 명령어 앞의 //를 없애고 두 군데에서 나타나는 password:와 pass:다음의 비밀 번호 해시는 앞 단계에서 복사해 둔 비밀 번호 해시로 바꿉니다.
// Securing Node-RED
// -----------------
// To password protect the Node-RED editor and admin API, the following
// property can be used. See http://nodered.org/docs/security.html for details.
adminAuth: {
type: "credentials",
users: [{
username: "admin",
password: "$2b$08$q9jgUlHa4acWMtPPBYQI0.DxrfKQuthuUuwecy2xhSZLlvAXmmSKm",
permissions: "*"
}]
},
// To password protect the node-defined HTTP endpoints (httpNodeRoot), or
// the static content (httpStatic), the following properties can be used.
// The pass field is a bcrypt hash of the password.
// See http://nodered.org/docs/security.html#generating-the-password-hash
httpNodeAuth: {user:"user",pass:"$2b$08$q9jgUlHa4acWMtPPBYQI0.DxrfKQuthuUuwecy2xhSZLlvAXmmSKm"},
httpStaticAuth: {user:"user",pass:"$2b$08$q9jgUlHa4acWMtPPBYQI0.DxrfKQuthuUuwecy2xhSZLlvAXmmSKm"},
// The following property can be used to enable HTTPS
// See http://nodejs.org/api/https.html#https_https_createserver_options_requestlistener
ctrl+o, Enter, ctrl+o를 차례대로 실행하면 수정된 파일이 보관됩니다.
Node-RED 다시 실행하기
node-red-restart

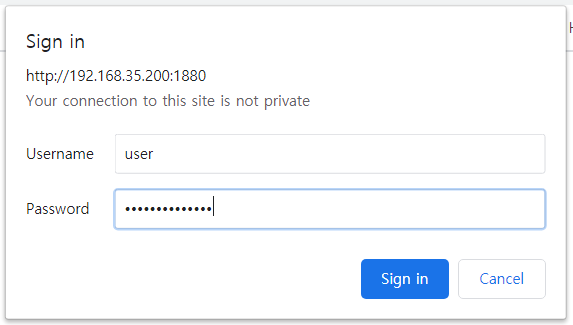
2 사용자와 비밀번호을 입력하여 로그인하기
http://node-red의IP:1880로 로그인할 때 사용자 ID admin와 비밀 번호gildongcoolguy을 입력해야 합니다.